Why Traditional QA Falls Short
Modern software development moves fast, with complex codebases, AI-assisted coding, and rapid release cycles. Manual QA and reactive testing can't keep up, leaving defects to slip through and impact users. Traditional reliability models are hard to apply in practice, requiring expert knowledge and often overlooking issues outside the testing phase.
Built for Predictable Delivery
Designed for engineering and QA teams, STAR supplements your workflow with predictive analytics—no expert knowledge needed.
Predict Readiness
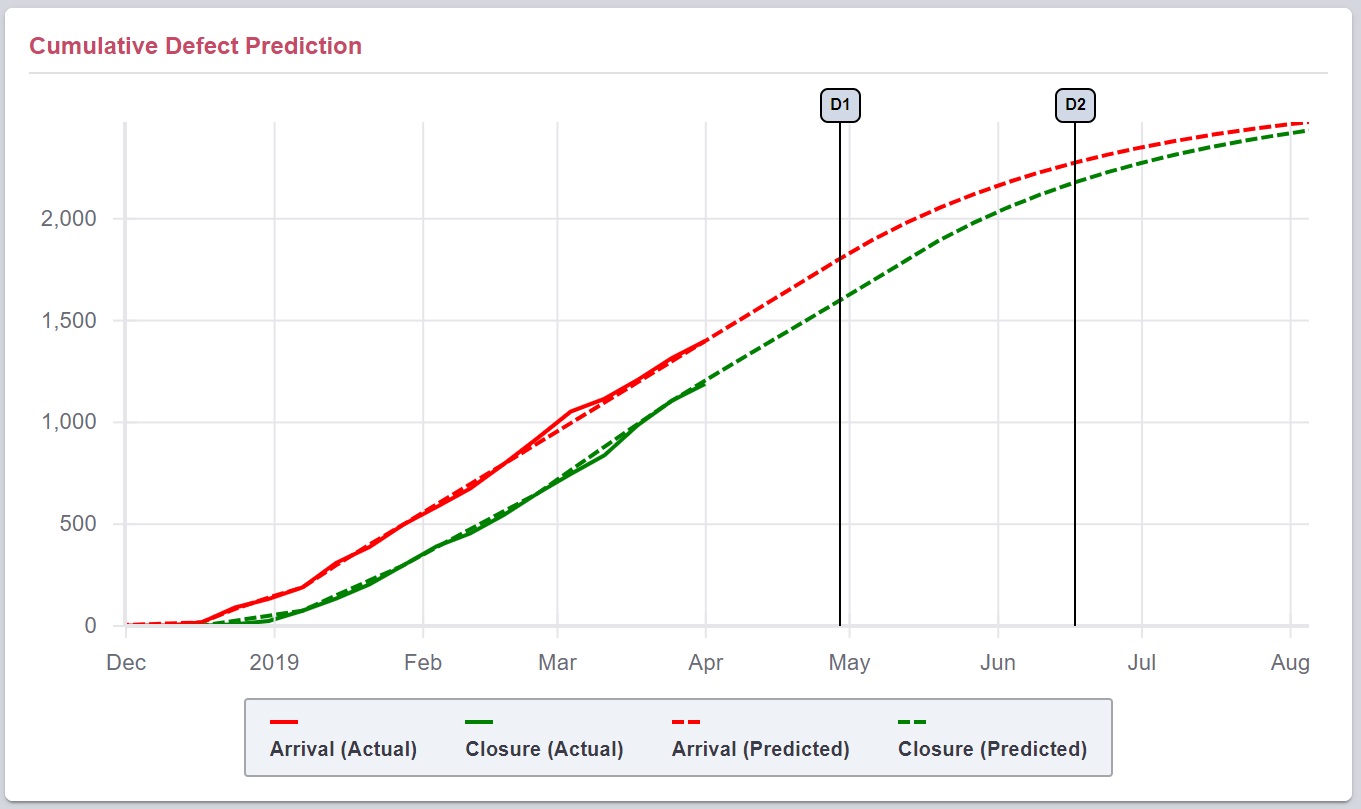
Know when your product will be ready and how many defects remain. Evaluations are available for both trial and commercial deployment projects.
Estimate Backlog
See how many additional defects may appear before release.
Component Insights
Identify which parts of your system are most defective and prioritize fixes.
Evaluate Changes
Explore how adding developers, adjusting delivery dates, or shifting scope impacts quality. Collaborate across teams to take corrective actions.
Plan with Confidence
Use previous release and effort data to anticipate software quality early, helping teams make informed decisions during project planning.
Data-Driven Decisions
Make informed, statistically sound decisions with STAR's predictive analytics.
Developer Productivity Gain
Developers spend less time fixing defects.
Faster Delivery
Schedule delays reduced, accelerating time to market.
EVR: A Simple Signal for Project Stability
Three Forces Converging to Create Exponential Risk
- •Embedded and IoT systems are becoming increasingly software-driven
- •Software size and system interactions continue to expand over time
- •Complexity is rising as functionality shifts from hardware to software
- •AI tools are now widely adopted by software developers
- •Development velocity is increasing as AI assists code creation
- •Faster code generation introduces new challenges for understanding and oversight
- •Billions of connected devices are in operation worldwide
- •Systems increasingly span edge, cloud, and distributed environments
- •Connectivity expands system scale and introduces new failure paths
These forces are accelerating defect introduction while detection capacity remains flat — EVR is climbing, signaling exponential risk to your schedule and budget.
EVR = defects entering ÷ defects fixed
EVR provides earlier warning than traditional metrics. When EVR exceeds 1.0, defects are accumulating faster than they're being resolved.
How STAR Works + Shift-Left
Turn defect and project data into real-time insights and corrective actions.
Defects
Track past and current defects
Project Milestones
Sprints and release dates
Development Plan Data
Team capacity and planned work
Data Pre-Processing
Organize and clean inputs
Defect Prediction
Forecast defects and backlog
EVR & Risk Trajectory
Calculate project health and backlog trends
Quality Metrics
Defect arrival, open predictions, residuals at delivery
Corrective Actions
Adjust release dates, add developers, shift scope to prevent late-stage defects (Shift-Left)
EVR Output
Shows project stability and whether defects are accumulating faster than resolution
EVR and shift-left insights empower teams to act early, reducing rework and improving delivery confidence.
STAR in Action
From preventing backlog growth to improving release quality, STAR helps teams predict issues early, allocate resources wisely, and deliver software with confidence.
Enhancing Software Reliability
Optimizing Resources for Success
Customer-Centric Quality Improvement
During Planning Phase
For every action recommended, STAR quantifies the expected effect on quality, backlog, and delivery risk.
System-Level Capabilities / Differentiators
STAR demonstrates proven predictive accuracy using real-world datasets from telecom and aerospace domains.